
The elements helium (He), neon ( Ne), argon ( Ar), krypton ( Kr), xenon ( Xe), and radon ( Rn) are placed in the zero group or group VIIIA of the periodic table. All the elements of this group are colourless monoatomic gases that can be liquified and solidified. These are called noble gases or, sometimes, rare gases.
Noble gases, or inert gases, belong to Group 18 of the periodic table. These elements are characterised by having filled outermost electron shells, which gives them high stability. Because of this stable electronic configuration, they are placed at the end of each period in the periodic table. Noble gases are monoatomic under normal conditions and play an important role in understanding atomic structure and periodic trends.
Occurrence and Properties
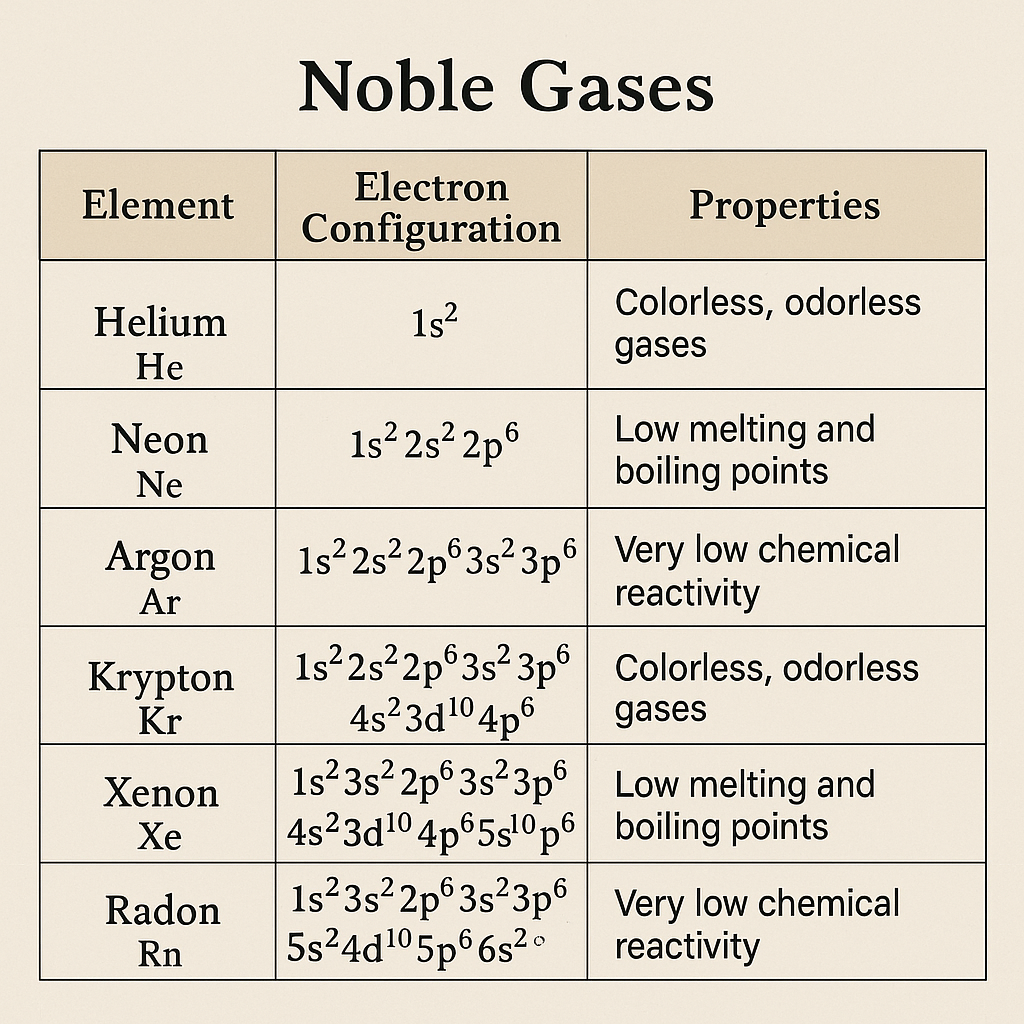
The noble gases occur as minor constituents of the atmosphere. Furthermore, the noble gases are isolated from air, either by fractional distillation or by some chemical method. The principal commercial sources of Ne, Ar, Kr, and Xe are air.
Helium
It is present on Earth as a result of radioactive decay. After hydrogen, it is the second most abundant element in the universe. Alpha particles are doubly ionised helium atoms, He²⁺. It is simple and economical to isolate the helium gas from certain natural gases by the liquefaction method.
Neon
It is 1/65000th part of the atmosphere, and it is also isolated during the liquefaction of air. In a discharge tube, neon glows reddish ( of all the noble gases, the discharge of neon is the most intense at ordinary voltage and current). Liquid neon has over 40 times more refrigeration capacity than liquid helium.
Argon
Argon is a colourless and odourless gas. It is very inert and not known to form any true chemical compounds. Moreover, it is obtained as a by-product during the liquefaction of air.
Krypton
Traces of krypton are present in the air. It is a colourless, odourless and fairly expensive gas. It is characterised by its brilliant green and orange spectral lines. Its compound, krypton difluoride, can be prepared by various methods.
Xenon
It is present in the atmosphere to a very small extent ( 0.08 ppm). It is obtained as a by-product during the fractional liquefaction of air. Xenon is available commercially in cylinders at high pressure. Such as it reacts with fluorine but not with water. However, it is slightly soluble in water to the extent of about 110 mL/lit at 20 °C.
Radon
It is the alpha-decay product of radium. Radon is present to a very small extent in the atmosphere, and it could be obtained as a by-product from the liquefaction of air. However, the small quantities of this gas can usually be collected from the radioactive decay of radionuclides.
Physical Properties
- The noble gases have valence shells which are closed octets (except He). Due to closed shells, their ionisation energy values are very high.
- They have low boiling points. The boiling point of helium is the lowest of any known substance. Their boiling points increase with increasing atomic number down the group.
- The very low values of melting and boling points and low heats of vaporization show that noble gases have weak forces of attraction between their atmos. AS there are no ordinary electron-pair interactions, these weak forces must be of the Vander Waals type.
- The solubility of the noble gases in water increases with increasing atomic number. This is because the bigger atoms are more readily polarised by water molecules.
Application of Noble Gases
Helium
- It is used in weather balloons, in welding and in traffic signal lights.
- A mixture of 80% helium and 20% oxygen is used for breathing by the scuba divers.
- It is used as a cooling medium for nuclear reactors.
Neon
- It is largely used in making neon advertising signs, in high-voltage indicators and TV tubes.
- Neon and helium are used in making glass lasers.
Argon
- It is used in electric light bulbs, in fluorescent tubes, in radion tubes and in Geiger counters ( used to detect radioactivity).
- Argon is also used for welding and cutting.
Krypton
- It is used to fill fluorescent tubes and in flash lamps for high-speed photography.
-
It is used in high-performance bulbs, like flashlights, camera flashes, and airport runway lights, because it gives a bright white light.
-
Krypton is used in krypton ion lasers, which are used in eye surgeries, scientific research, and some industrial applications.
Xenon
- It is used in bactericidal lamps.
-
It is used in high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps, especially in car headlights, for bright, white light.
-
Moreover, gas is used as a general anaesthetic in some medical procedures because it is non-toxic and safe for the brain.
Radon
- Radon, being radioactive, is used in radiotherapy for cancer and earthquake prediction.
Conclusion
Noble gases are unique elements with stable electronic configurations that make them chemically inactive. Their distinct position in the periodic table highlights their importance in understanding atomic structure and chemical trends. Similarly, being inert, they play key roles in lighting, welding, and medical applications.


